Main Results
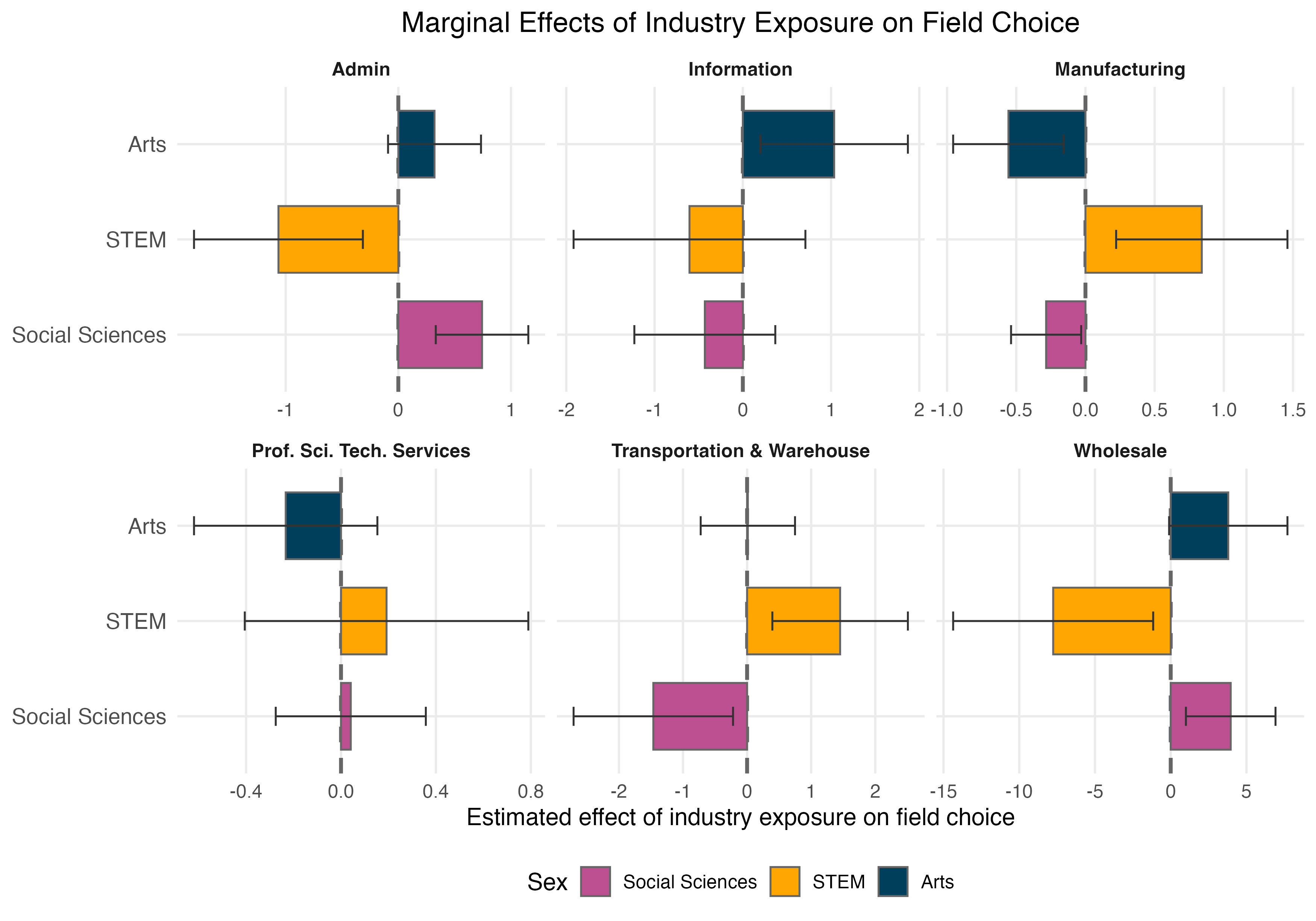
Percentage Point Changes in Probability of Field Choice
Multinational Presence Shapes College Major Choice
November 24, 2025
Lower- and Middle-Income Countries (LMICs) have seen an increasing rate of fdi inflow in recent decades
Source: World Bank
Tertiary enrollment rates have increased in LMICs
Source: World Bank
Hypothesis: Multinational Firms affect skill specialization decisions
Identification Strategy
Mechanism of fdi shifting human capital specialization decisions
Determinants of College Major Choice
Effects of increased trade/fdi inflow on local labor markets
Mechanism of fdi shifting human capital specialization decisions
Determinants of College Major Choice
Effects of increased trade/fdi inflow on local labor markets
Mechanism of fdi shifting human capital specialization decisions
Determinants of College Major Choice
Effects of increased trade/fdi inflow on local labor markets
Education
Public universities require applicants to list their two preferred majors when applying Example
Multinational Firms
Costa Rica incentivizes FDI inflows through dedicated Free Trade Zone (FTZ) regime

Major Choice Data
STEM & Applied Sciences
Soc. Sci. & Prof. Studies
Arts, Writing, & Service
Multinational Firms
Individuals Utility from Studying in Field of Study (m) is:
\[\begin{equation} U_{idmt} = \beta_{m} \Gamma_{djt} + \gamma_{i}X^{'}_{i} + \alpha_{c} + \alpha_{t} + \varepsilon_{idmt} \end{equation}\]
Subscripts
\(i =\) individual, \(\; d =\) district-of-residence, \(\; m =\) field of study, \(\; j =\) industry, \(\; c =\) canton, \(\; t =\) year
\[\begin{align} \Gamma_{djt} = p_{mjt} \times \left(\sum_{d'}\sum_{j} \dfrac{\text{Tenure}_{k(j),d't}}{exp(\text{dist}_{dd'})} \right) \end{align}\]
Subscripts
\(d =\) district-of-residence, \(\; d' =\) district-of-operation, \(\; k(j) =\) firm \(\,k \,\) in industry \(\, j\), \(\; t =\) year
\(\text{Tenure}_{k(j),d't}\): Tenure of firm captures how long individual has been aware/exposed to presence of MNC
\(exp(\text{dist}_{dd'})\): Distance (in km) from student-district to firm-district
\(p_{mjt}\): Industry Attachment Probabilities
Estimate the effect of MNC presence on student field of study choice by using a Multinomial Logit Model and then estimating the Average Marginal Effects (AMEs) for each industry
This produces estimates that tell us how much the probability of choosing a particular major changes when the MNC Presence Index increases by one unit
Interpretation
In this model, this is interpreted as an additional firm-year in the student’s district of residence, which is either a new firm entering or an existing firm maturing
I also report the distance decay of the effects, showing how distance diminishes the presence effects
I then report results by exposure level differences
Percentage Point Changes in Probability of Field Choice
Percentage Point Changes in Probability of Field Choice
Trends remain largely similar across industry and field with significantly small coefficients
Multinational Presence Shapes College Major Choice